The information below is taken from the instruction sheet issued by the Canada Revenue Agency.
Instructions
If an election has been made under paragraph 261(3)(b) of the Income Tax Act to report in a functional currency, state all monetary amounts in that functional currency, otherwise state all monetary amounts in Canadian dollars (no cents).
Part II – Non-resident information
Q.1 and Q.2. Enter the name and address of the non-resident. For the list of country codes, see the CRA publication, T4061 – NR4 – Non-Resident Tax Withholding, Remitting and Reporting guide, Appendix A – Country Codes, at: cra.gc.ca/E/pub/tg/t4061/t4061-e.html.
Q.3. State the type of relationship that exists between the reporting person/partnership and the non-resident. The Canada Revenue Agency needs the relevant financial statements (in English or French) of the non-resident if the non-resident is controlled by the reporting person or partnership and is resident in a non-treaty country. Canada has income tax conventions (treaties) with more than 60 countries. These include the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Japan, and Australia. For information about the countries with which Canada has concluded an income tax treaty, contact your tax services office or consult the Internet at: fin.gc.ca.
Q.4. State the main business activities for the transactions reported in Part III by entering the appropriate North American Industrial Classification System (NAICS) codes. The current NAICS codes can be found at the Statistics Canada internet site, https://www23.statcan.gc.ca/imdb/p3VD.pl?Function=getVD&TVD=1369825. You can enter more than one code.
Q.5. State the main countries for the transactions reported in Part III by entering the appropriate country code. You can enter more than one code. For the list of country codes, see the information provided under Q1. and Q2. above.
Q.6. Enter yes or no to the question. In general, subsection 247(4) of the Income Tax Act relates to the requirement to maintain and make available contemporaneous transfer pricing documentation. You can find more information on contemporaneous documentation requirements in Information Circular 87-2, International Transfer Pricing. The circular is available at our tax services offices and on the Internet at: canada.ca/taxes.
Part III – Transactions between reporting person/partnership and non-resident
Enter (to the nearest Canadian dollar/functional currency unit if applicable) the monetary consideration derived or incurred for the transactions in Part III. Only record in Part III those amounts that apply to the non-resident described in Part II. Report gross amounts in the two columns.
The “Sold to non-resident” and “Revenue from non-resident” refers to gross sales and revenue received from non-arm’s length transactions with non-residents. For example, this includes transactions related to exports from Canada and services provided to the non-resident.
The “Purchased from non-resident” and “Expenditure to non-resident” refers to gross purchases and expenditures made relating to non-arm’s length transactions with non-residents. For example, this includes transactions related to imports into Canada and services provided by the non-resident.
For the banking industries, the line for “Stock in trade/raw materials” must be used to report bonds, debentures, loans, mortgage transactions. The normal interest income and expense on loans and advances with the non-arm's length non-resident(s) must be reported in the Financial section.
Part V – Derivatives
The column for Notional Amounts applies to swap transactions. The terms used in this section are described below:
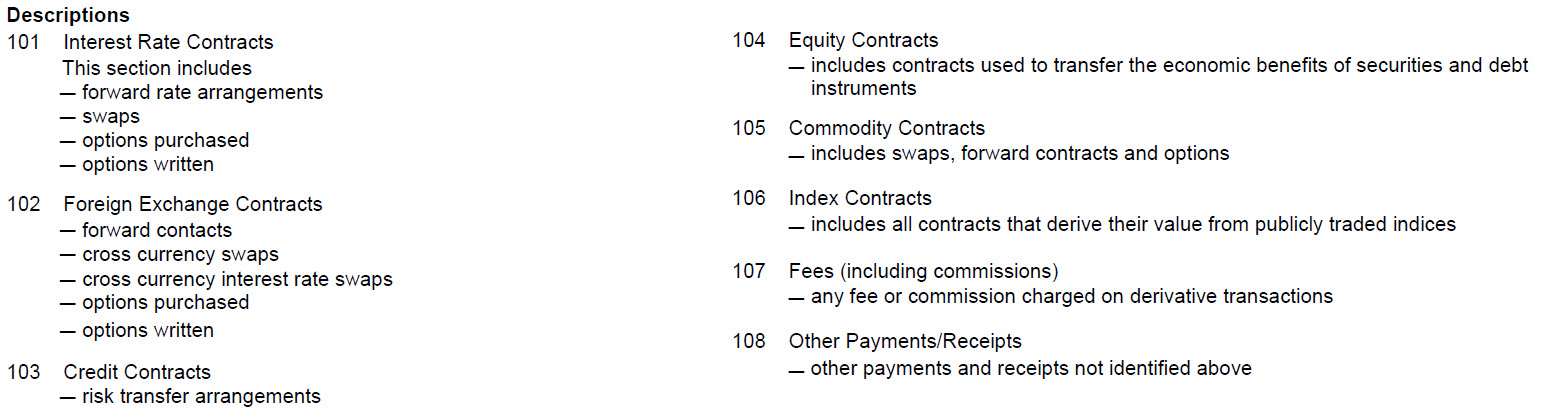
Descriptions
|
101 Interest Rate Contracts This section includes – forward rate arrangements – swaps – options purchased – options written 102 Foreign Exchange Contracts – forward contracts – cross currency swaps – cross currency interest rate swaps – options purchased – options written 103 Credit Contracts – risk transfer arrangements |
104 Equity Contracts – includes contracts used to transfer the economic benefits of securities and debt instruments 105 Commodity Contracts – includes swaps, forward contracts and options 106 Index Contracts – includes all contracts that derive their value from publicly traded indices 107 Fees – any fee or commission charged on derivative transactions 108 Other Payments / Receipts – other payments and receipts not identified above |
Do you need more information?
For general enquiries, contact the Business Enquiries section of your tax services office. For detailed information about completing the form, contact the International Audit Division of your tax services office. The address and telephone number of the tax services office are listed under "the Canada Revenue Agency" in the Government of Canada section of your telephone book and on the Internet at: canada.ca/taxes.
Instructions
If an election has been made under paragraph 261(3)(b) of the Income Tax Act (Act) to report in a functional currency, state all monetary amounts in that functional currency, otherwise state all monetary amounts in Canadian dollars. Round all monetary amounts to the nearest Canadian dollar or functional currency unit, if applicable. Only certain corporations can elect to report in a functional currency. See the CRA publication Income Tax Folio S5-F4-C1, Income Tax Reporting Currency at: canada.ca/cra-income-tax-reporting-currency.
Part II – Non-resident information
Q.1., Q.2. and Q.3. Enter the name, TIN and address of the non-resident. For the list of country codes, go to canada.ca/cra-country-codes.
Q.4. State the type of relationship that exists between the reporting person/partnership and the non-resident. The CRA needs the relevant financial statements (in English or French) of the non-resident if the non-resident is controlled by the reporting person or partnership and is resident in a non-treaty country. Canada has income tax conventions (treaties) with more than 90 countries. These include the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Japan, and Australia. For information about the countries with which Canada has concluded an income tax treaty, go to canada.ca/en/department-finance/programs/tax-policy/tax-treaties.
Q.5. State the main business activities for the transactions reported in Part III by entering the appropriate NAICS codes. The current NAICS codes can be found at https://www23.statcan.gc.ca/imdb/p3VD.pl?Function=getVD&TVD=1369825. You can enter more than one code.
Q.6. State the main countries for the transactions reported in Part III by entering the appropriate country code. You can enter more than one code. For the list of country codes, see the information provided under Q1., Q2. and Q3. above.
Q.7. Enter yes or no to the question. In general, subsection 247(4) of the Act relates to the requirement to maintain and make available to the Minister contemporaneous transfer pricing documentation. You can find more information on contemporaneous documentation at canada.ca/cra-transfer-pricing by going to the "Documentation Requirements" section and clicking on the "contemporaneous documentation" link.
Part III – Transactions between reporting person/partnership and non-resident
Enter the amount (rounded to the nearest Canadian dollar or functional currency unit, if applicable) for the transactions in Part III. Only record in Part III those amounts that apply to the non-resident described in Part II. Report gross amounts in the two columns.
The "Sold to non-resident" and "Revenue from non-resident" refers to gross sales and revenue received from non-arm's length transactions with non-residents. For example, this includes transactions related to exports from Canada and services provided to the non-resident.
The "Purchased from non-resident" and "Expenditure to non-resident" refers to gross purchases and expenditures made relating to non-arm's length transactions with non-residents. For example, this includes transactions related to imports into Canada and services provided by the non-resident.
For the banking industries, the line for "Stock in trade/raw materials" must be used to report bonds, debentures, loans, mortgage transactions. The normal interest income and expense on loans and advances with the non-arm's length non-resident(s) must be reported in the Financial section.
Part IV – Indebtedness, investments and similar amounts
Subsection 15(2) of the Act can apply to a non-resident shareholder of a Canadian resident corporation, in which case, the debt is treated as a deemed dividend subject to non-resident withholding tax. Where a corporation resident in Canada (CRIC) is controlled by a non-resident corporation, subsection 212.3(2) of the Act contains similar rules (the foreign affiliate dumping rules) to deem certain amounts owing by a foreign affiliate of the CRIC to be a dividend paid to the non-resident shareholder.
The election to treat the debts as a PLOI, is a choice the non-resident shareholder and the CRIC can make to avoid the deemed dividend treatment and the withholding tax liability that would otherwise result. You can find more information on PLOI, at canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/tax/businesses/topics/corporations/corporation-payments/understanding-interest.html#Ins.
State whether a PLOI election was made and if so, provide the deemed interest amount included as taxable income for the tax year or fiscal period.
Part V – Derivatives
The column for "Notional Amount" applies to swap transactions. The terms used in this section are described below:
Do you need more information?
If you need more information, go to canada.ca/taxes or call 1-800-959-5525 for business enquiries, or 1-800-959-8281 for individual enquiries. For detailed information about completing the form, contact your tax services office (TSO). TSO contact information can be found at canada.ca/cra-tso-contact-information.
See Also: