Taxprep Development Toolkit Instructions
With the Taxprep Development Toolkit, all cells of the Taxprep program are available through an outside application. A Microsoft Excel Worksheet example is available here. This worksheet example can help you developing your own Taxprep integration.
Functions and Attributes Available through the COM Interface
You can access the following information through the Excel worksheet provided as an example
- In the Visual Basic Editor, add a reference to the library using the menu option Tools\References, then select Taxprep Base COM Interfaces and press OK
- Select the menu option View\Object Browser, then select the T1TxpCom from the combo box (see below)
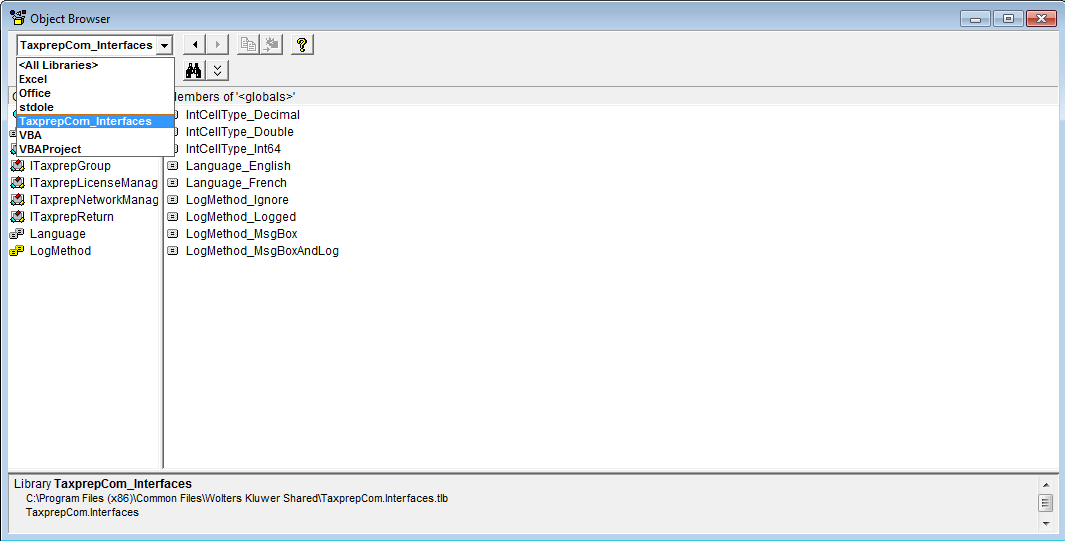
Access to Cell Functions and Properties
These functions and properties can be used to access or modify the attributes of a cell.
Members of “ITaxprepCell”
- Property Choices As Variant
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Array of strings containing the choices available for this translated string cell (using the current DataLang specified for the return) Returns the empty value if there are no choices for this cell - Property Description As String
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Description text for the cell (using the return\ MsgLang) - Property HasCalc As Boolean
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Does the cell have a default calculation? - Property HasInput As Boolean
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Does the cell have user input? - Property IsEmpty As Boolean
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Is the cell empty? - Property IsOverridden As Boolean
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Has the default calculation for this cell been overridden? - Property IsProtected As Boolean
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Can the value be altered? - Property IsSelectable As Boolean
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Is a selection dialog available for this cell? - Property Name As String
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
The cell\ full name - Property OwnerReturn As TaxprepReturn
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
The return that owns this cell - Function GetValue() as Variant
Member of T1TxpComITaxprepCell
Returns the value of a cell - Function SetValue() as Variant
Member of T1TxpComITaxprepCell
Set the value of a cell - Sub DoSelection()
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Displays a dialog with the available choices for the cell - Sub RemoveOverride()
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
If the cell is overridden, this method removes the overridden state and clears the cell\ value, allowing the default calculation to be restored the next time the return is calculated.
- Function CreateAttachedSchedule() As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Creates an attached schedule for the cell. Returns true if successful. Note that function fails if the cell already has an attached schedule. - Sub DeleteAttachedSchedule()
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
The cell's attached schedule is deleted completely and the cell will no longer have an attached schedule. - Function GetAttachedSchedule(out RepeatNum as Variant) As ITaxprepGroup
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Returns the group and the 1-based repeat number of the attached schedule for the cell. - Property HasAttachedSchedule As Boolean read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepCell
Does the cell have an attached schedule ? - Sub UnlinkAttachedSchedule()
Member of T1TxpComITaxprepCell
The cell's attached schedule becomes an unattached schedule and the cell no longer has an attached schedule (useful if you do not want to lose the information on an attached schedule).
Access to Group Functions and Properties
These functions and properties can be used to access or modify the attributes of a logical group of cells.
Members of “ITaxprepGroup”
- Property MaxRepeats As Long
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepGroup
The maximum number of repeats allowed for the group - Property MinRepeats As Long
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepGroup
The minimum number of repeats allowed for the group - Property Name As String
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepGroup
The full name of the group - Property NumRepeats As Long
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepGroup
The current number of repeats for the group - Function CanDeleteRepeat (Position As Long) As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepGroup
Determines whether the specified 1-based repeat number can be deleted using DeleteRepeat. Returns true if the repeat can be deleted and false otherwise. - Function CreateRepeat([NumNewRepeats As Long = 1], [Position As Long = -1]) As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepGroup
Creates repeat(s) at the specified insertion point. The new repeats are inserted in front of the specified position (1 to NumRepeats) or at the end if the default value of 1 is used. - Function DeleteRepeat(Position As Long, [NumToDelete As Long = 1]) As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepGroup
Deletes repeat(s) at the specified position (1 to NumRepeats). If the function returns true, then all specified repeats were deleted. If the function returns false, this means that no repeats were deleted. The function could return false for a variety of reasons including if any of the parameters are invalid, if the return is read-only or if the system determines that one or more of the repeats cannot be deleted. Use CanDeleteRepeat if you need to determine in advance whether a specific repeat can be deleted. - Function GetRepeatID (RepeatNum As Long) As String
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepGroup
If you need to store a repeat number in an external file or database, it is much safer to store the ID of the repeat rather than the actual repeat number since repeats can be added and removed and the repeat numbers may not be the same the next time the taxprep return is accessed using COM. Returns an empty string if the specified 1- based RepeatNum is not valid. - Function GetRepeatNumFromID(RepeatID As String) As Long
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepGroup
Use this function to determine the current 1-based repeat number for a given RepeatID (which was likely previously obtained using GetRepeatID). Returns 1 if the specified RepeatID could not be found (for example if the repeat with the specified ID has been deleted since the RepeatID was obtained).
Licence Manager Identification
A Taxprep Integration Partner can purchase a runtime licence key that will allow COM access to a specified application even on computers for which the COM module has not been purchased/activated. This is the interface to use if you have such a runtime licence key.
- Function CreateNetworkManager
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepLicenceManager
Use this method to create an ITaxprepNetworkManager if you have a Runtime Licence key to access the desired COM TaxprepReturn. - Function CreateTaxReturn
Member of T1TxpCom ITaxprepLicenceManager
Use this method to create an TaxprepReturn if you have a Runtime Licence key to access the desired COM TaxprepReturn
Network User Identification
This function provides the user ID and password required to use the appropriate user profile when creating a return.
Members of “ITaxprepNetworkManager”
- Function CreateReturnAsUser(NetworkUserName As String, NetworkPassword As String) As TaxprepReturn
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
If you use the Network version of the application, use this function to create a return as a specific user. This ensures that the settings for the specified user (including the tax preparer profiles and rates tables) are used for the return
Access to Return Functions and Properties
These functions and properties can be used to open, save, calculate a return, set and get cell values…
Members of “TaxprepReturn”
- Property DataLang As Language
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Language used for translated string cells when using GetCellValue and SetCellValue (Default: Language_English) - Property DataLocked As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Specfies whether to prevent data from being altered in the return - Property IntCellVarType As IntCellType
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
This property is used to control the type of COM variant value obtained when gettin g the value of an Integer cell, which is an Int64 internally. Default: IntCEllType_Decimal - Property LogMethod As LogMethod
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Specifies how cell error and warning messages are provided. Default: LogMethod_MsgBox - Property MsgLang As Language
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Language that should be used in messages and dialog boxes. Default: Language_English - Property NullForEmptyCells As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
When the tax cell is empty, this property controls whether GetCellValue returns the "zero" value for the cell (false for booleans, 0 for numerics, etc ) or whether it returns the speical NULL variant value Default: False - Property NumLogMessages As Long
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
The number of messages in the log - Property PasswordProtected As Boolean
Read-only
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
s this data file protected by a password? - Property UseDecimalForCurrency As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
When getting values for monetary cells, the variant returned containing the value is normally a Currency. If your programming environment does not support the Currency type, set this property to true to get the value as a Decimal instead - Sub Browse()
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Browse the groups, cells and available short cell names for the return in an Explorer-like window - Sub BrowseAllCellNames()
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Browse all possible cell names in all possible groups (this differs from Browse in that this function browses an empty return and this function includes at least one copy of every possible group so that you can see every possible cell name) - Sub Calculate()
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Calculate the return - Function ChangePassword(OldPassword As String, NewPassword As String) As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Changes the password for the client file to the desired value. You require the existing password to do this Returns false if the client file has a password and it does not match the CurrentPassword parameter - Sub ClearMessageLog()
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Empties the message log - Function GetCell(CellName As String, [CreateRepeats As Boolean = False], [MsgOnFail As Boolean = True]) As TaxprepCell
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Get a cell - Function GetCellDescription(CellName As String) As String
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Returns the cell description (if available) using the current MsgLang The function will still succeed if the CellName contains repeat numbers that don’t exist yet in this return - Function GetCellValue(CellName As String)
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Get value of a cell (translated string cells use the DataLang property) - Function GetGroup(GroupName As String, [CreateRepeats As Boolean = False], [MsgOnFail As Boolean = True]) As ITaxprepGroup
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Get a cell group - Function Open(FileName As String, [Password As String]) As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Open a tax return file If an empty string is provided as the FileName, a standard File/Open dialog is presented - Function RemovePassword(CurrentPassword As String) As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Removes the password from the client file You require the existing password to do this Returns false if the client file has a password and it does not match the CurrentPassword parameter - Function Save() As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Save the return to same file For new returns, a standard File/Save dialog is presented - Function SaveAs(FileName As String) As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Save the return to a new file. If an empty string is provided as the FileName, a standard File/Save dialog is presented - Sub SaveMessageLog(FileName As String, [ClearAfter As Boolean = False])
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Save message log to a text file with option to clear the log afterwards - Function SetCellValue(CellName As String, Value, [CreateRepeats As Boolean = True]) As Boolean
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Set the value of a cell (translated string cells use the DataLang property) To clear the cell, provide the special variant value of Null - Sub ShowMessageLog()
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Shows the messages in the log in a dialog box with option to save to a text file
- Function GetRepeatFromRepeatID(RepeatID As String, out RepeatNum As Variant)
As ITaxprepGroup
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Find the group/repeat in the tax return that has the specified RepeatID. Will return an empty variant if the specified RepeatID cannot be found (for example, the repeat may have been deleted since the RepeatID was obtained). If the repeat is found, the 1-based repeat number of the repeat is returned in the RepeatNum output parameter.
- Sub CloseFileHandle()
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
When working with TaxprepReturn TaxprepReturn under .NET, there can be a significant delay before the .NET garbage collector releases the COM TaxprepReturn, even after there are no further references on the TaxprepReturn. This can result in a tax return file remaining locked by the COM TaxprepReturn after it is no longer in use, preventing other users from working with the file. To solve this problem, you can use the .NET method "ReleaseComTaxprepReturn" to force the final cleanup of the COM TaxprepReturn or you can use this method to release the open file handle. If you use this method, we assume that you are done with the file and you will no longer be able to use the Save method. - Function GetAttachedSchedule(Index As Long, out RepeatNum As Variant, out Cell As Variant) As TaxprepReturn
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
Obtains the group and 1-based repeat number of the desired attached schedule. Also provides the cell to which the schedule is attached. Index must be in the range 1 to NumAttachedSchedules. - Property NumAttachedSchedules As Long
read-only
Member of T1TxpCom TaxprepReturn
The number of schedules attached to cells in the return.
Cell Type Options
Enum InteCellType
Member of T1TxpCom
Used to specify the type of Variant returned when obtaining the value of an Integer cell (which is an Int64 internally)
Members of InteCellType
- Const IntCellVarDecimal = 0
Member of T1TxpCom InteCellType
This is the default The Int64 value of the integer cell is returned as a 12-byte DECIMAL variant which can represent an Int64 precisely The DECIMAL type is supported in all versions of Windows and recognized by a variety of programming languages, including Visual Basic 6 0 - Const ntCellType_Decimal = 2
Member of T1TxpCom InteCellType
The Int64 value of the integer cell is returned as a DOUBLE variant value. Note that the DOUBLE subtype of the COM variant cannot represent large Int64 values precisely. You should therefore use this option only if the data types supported by your programming language don't give you any other choice - Const IntCellType_Int64 = 1
Member of T1TxpCom InteCellType
The Int64 value of the integer cell is returned as an INT64 variant value. Note that the INT64 subtype of the COM variant was not part of the original COM specification is there not supported by all versions of Windows This option is useful if you are using a NET programming language since they support Int64 directly within the language
Language Options
Enum Language
Member of T1TxpCom
Used to specify languages for various functions
Members of Language
- Const Language_English = 0
Member of T1TxpCom Language
Used to specify English in the SetCellValue and GetCellValue functions - Const Language_French = 1
Member of T1TxpCom Language
Used to specify French in the SetCellValue and GetCellValue functions
Logging Options
Enum LogMethod
Member of T1TxpCom
The various ways that error and warning messages can be provided
Members of LogMethod
- Const LogMethod_Ignore = 3
Member of T1TxpCom LogMethod
Error and warning messages are discarded. Pay attention to the return value from SetCellValue so that you can provide your own feedback. - Const LogMethod_Logged = 1
Member of T1TxpCom LogMethod
Error and warning messages are added to the message log which can be viewed with ShowMessageLog. - Const LogMethod_MsgBox = 0
Member of T1TxpCom LogMethod
Error and warning messages are shown in a Message Box immediately - Const LogMethod_MsgBoxAndLog = 2
Member of T1TxpCom LogMethod
Error and warning messages are shown in a Message Box immediately and also added to the log
How to use the Taxprep Development Toolkit in a .NET application
To be able to leverage the IntelliSense functionality for types/interfaces/methods that are exposed by the COM assembly, a reference to the COM must be added in the project:
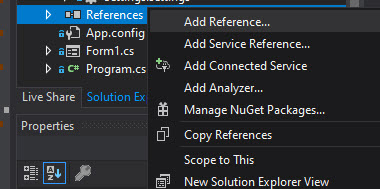
- In your project, right-click References and select Add Reference.
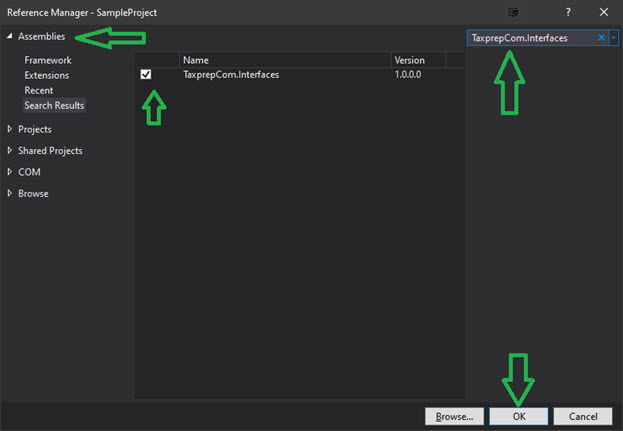
- On the left panel, select Assemblies then search for TaxprepCom.Interfaces and add this reference.
Once the reference is added, you will need to instantiate the appropriate ComFactory class. This class implements IDisposable and needs to be disposed of after use.
In files where you want to use the com, add a reference to the added dll interface by means of a using statement:

NOTE: Since this class works with a separate AppDomain, classes that are created by this factory are meant to be used upon instantiation and not kept for reuse as they eventually will be disposed of automatically after a given period of inactivity. A good way to ensure that the objects are used in a limited scope and do not become stale prior to use is to leverage the “using” statement when creating the factory. This helps you understand/see that objects created with the help of the factory are locally-scoped references within the using scope and also ensures that the factory is properly disposed of upon exiting the scope.
Here is an example of instantiation of the COM factory:
private void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (var aFactory = new TaxprepComFactory("TaxprepT2.Return.2019v2"))
{
//your code leveraging this com would go here...
}
}
Note: The TaxprepComFactory object expects a ProgId as the argument in its constructor. The ProgIds follow the naming structure below: Product.Type.Version, for example, TaxprepT2.Return.2019v2 or TaxprepT1.Return.2019, etc.
CreateTaxprepReturn():
This call returns an ITaxprepReturn interface. From there, the same methods/members as the COM are available.
CreateTaxprepNetworkManager():
This call returns an ITaxprepNetworkManager interface. From there, the same methods/members as the COM are available.
CreateTaxprepLicenseManager():
This call returns an ITaxprepLicenceManager interface. From there, the same methods/members as the COM are available.
NOTE: If you have control over the application that will use the COM, an added step is necessary in order to leverage the pre-optimized calc libraries that were prepared during the initial installation of the Taxprep application. You need to specify the LoaderOptimization attribute on your application’s main method as follows, otherwise, this interpretation/optimization of the calculation libraries will be done on first call of CreateTaxprepReturn() (or equivalent call) for a given ComFactory instance. While this can take some time, all subsequent actions in the scope of that same factory instance will be performed in a timely fashion.
Example:
static class Program
{
/// <summary>
/// The main entry point for the application.
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
[LoaderOptimization(LoaderOptimization.MultiDomain)] <========= like this
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
}